Leave Your Message
Understanding the fundamentals of circuit components is essential for anyone embarking on the journey of electronics. Whether you're a complete beginner or someone looking to refresh your knowledge, identifying and comprehending these crucial elements can significantly enhance your ability to build and troubleshoot circuits. Circuit components, such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, each have distinct roles that contribute to the overall function of electronic devices. By grasping how these components work together, you can develop a deeper insight into the behavior of electrical systems and their applications.
In this guide, we will explore the most common circuit components encountered in basic electronics. We will break down their functions, characteristics, and significance in circuit design. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you will gain valuable skills that empower you to analyze and create your own electronic projects. This foundational knowledge not only serves as the building block for more advanced concepts but also fosters confidence in your ability to engage with the world of electronics effectively.

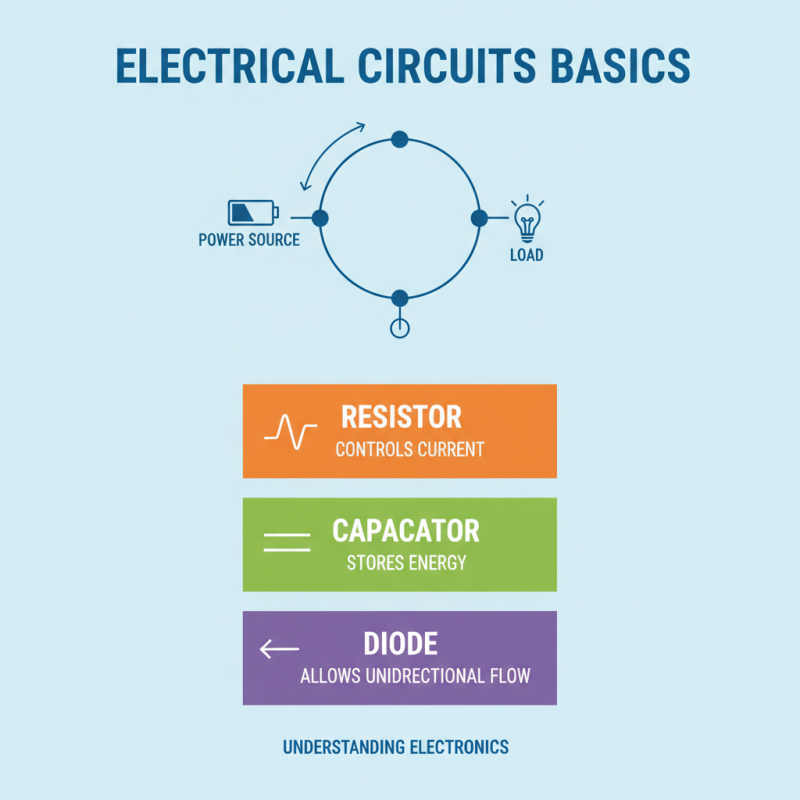
Understanding the basics of electrical circuits is essential for anyone looking to delve into the world of electronics. At its core, an electrical circuit is a pathway that allows electric current to flow, driven by a power source. Familiarity with the fundamental components—such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes—can significantly enhance one's understanding of circuit behavior and function. Resistors control the flow of current, capacitors store energy, and diodes allow current to flow in one direction only, each playing a vital role in the circuit's operation.
Tips: Start by creating simple circuits using a breadboard. This practice allows you to physically connect components and observe how they interact. Take notes on how each component affects the circuit's performance. Moreover, consider online simulations that let you experiment with circuits virtually; these tools can clarify complex concepts without the risk of damaging components or creating short circuits.
Additionally, understanding the terminology used in electrical engineering, such as voltage, current, and resistance, will greatly aid in learning. These terms define how much electric charge is flowing, the force pushing it, and how much it is impeded, respectively. Learning to read circuit diagrams, which use standardized symbols, will further enhance your ability to analyze and build circuits effectively. Engaging with community forums or joining local maker groups can also provide valuable insights and encouragement as you navigate the fundamentals of circuit design.
Identifying common circuit components is essential for beginners who wish to delve into the world of electronics. Among the most frequently encountered components are resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Resistors limit the flow of electric current, thus controlling voltage and current levels in a circuit. They can be found in various types and values, which are critical for protecting sensitive components and ensuring the desired operation of electronic devices.
Capacitors, on the other hand, store and release electrical energy. They are essential for smoothing out voltage fluctuations in power supply circuits and are often used in timing applications. Understanding the role of capacitors involves recognizing different types such as ceramic, electrolytic, and film capacitors, each serving specific purposes in electronic circuits. Inductors, meanwhile, store energy in a magnetic field when current passes through them and are commonly employed in filtering and energy storage applications. By becoming familiar with these components and their functions, beginners can build a strong foundation in understanding more complex circuit designs.
Resistors are fundamental components in circuit design, serving a crucial role in controlling the flow of electrical current. By providing resistance, they help to ensure that the current remains within safe limits, thus protecting sensitive components from damage. Resistors can be found in various configurations, such as in series or parallel arrangements, which allows designers to manipulate the overall resistance and voltage within a circuit. Through understanding Ohm's Law, beginners can grasp how resistors affect voltage, current, and power within a circuit.
In addition to their protective function, resistors are also essential for controlling circuit behavior. They can be used to set biasing conditions for transistors, divide voltages, or create specific time constants in timing circuits. The ability to choose the right resistor value is fundamental in achieving the desired performance and functionality of a circuit. By learning to identify resistor markings and understand their varying types—such as fixed, variable, or —beginners can effectively incorporate these components into their designs to achieve reliable and efficient circuits.
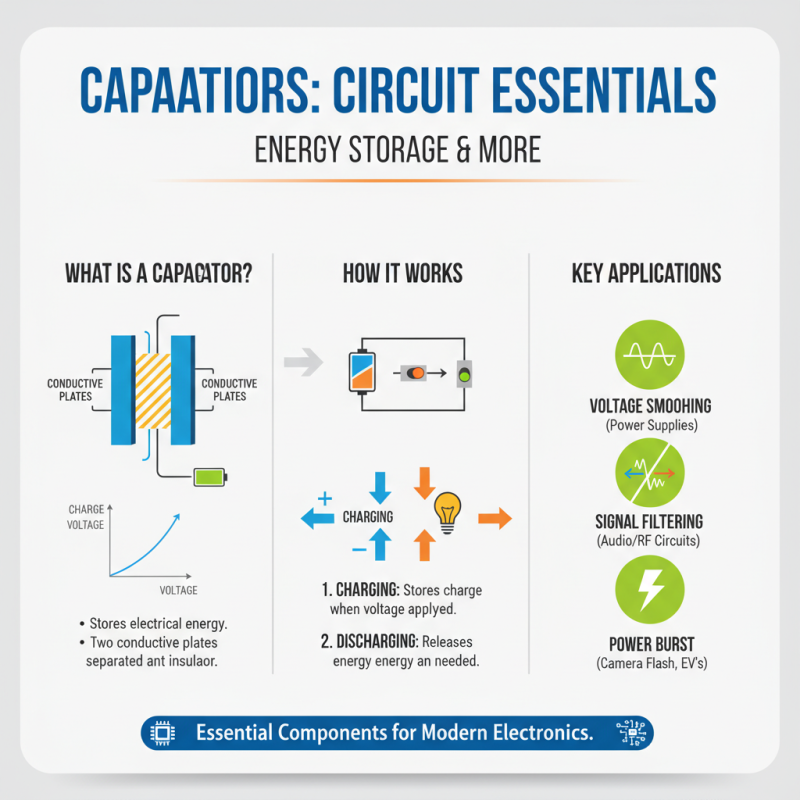
Capacitors play a vital role in many electronic circuits, acting as energy storage devices that temporarily hold electrical energy. When voltage is applied, they store charge on plates separated by an insulator or dielectric. This stored energy can then be released to smooth out fluctuations in voltage, filter signals, or provide a burst of power when needed. Understanding how capacitors work and their applications can greatly enhance your grasp of circuit design.
Tips for beginners include always noting the capacitance value and voltage rating of capacitors when working on a circuit. This ensures that you select the right component to handle the expected electrical load without risk of damage. Additionally, remember that capacitors can be polarized; for example, electrolytic capacitors must be connected in a specific direction. When troubleshooting circuits, observing how capacitors interact with other components can provide clues about system functionality.
Familiarize yourself with the different types of capacitors, such as ceramic, film, and tantalum, each serving unique purposes in circuit applications. For example, ceramic capacitors are often used for decoupling and filtering, while tantalum capacitors are favored in space-constrained designs due to their high capacitance density. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions when designing or repairing electronic circuits.
Inductors are fundamental components in electrical circuits, playing a crucial role in storing energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. They consist of a coil of wire wound around a core, which can be either air or a ferromagnetic material. The primary function of an inductor is to oppose changes in current, a behavior governed by Lenz's Law. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, it induces a voltage that opposes that change, thereby stabilizing the current in the circuit. This property makes inductors essential in applications such as power supplies, filters, and oscillators.
The characteristics of inductors are determined by several factors, including inductance, resistance, and the core material. Inductance, measured in henries (H), quantifies the inductor's ability to store magnetic energy. Each inductor has a specific inductance value that indicates how effectively it can resist changes in current. Additionally, the resistance of the wire used in the coil affects the efficiency and thermal performance of the inductor. The core material influences the inductance value and the saturation point, which is the maximum magnetic field the core can handle before becoming ineffective. Understanding these characteristics helps beginners grasp how inductors function within various electronic circuits and their significance in controlling current and voltage levels.
This bar chart illustrates the key specifications of inductors, focusing on their inductance (in henries), direct current resistance (in ohms), current ratings (in amperes), and voltage ratings (in volts). Understanding these parameters is crucial for beginners when selecting and analyzing inductors in circuits.